Will You Pay Higher Taxes in Retirement?
Your Social Security income and RMDs will most likely combine to deliver a tax torpedo, but there are ways to reduce your income in retirement to pay less tax.

Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Have you ever heard the saying, “You will pay less tax in retirement”? Well, most of our clients do not pay less tax in retirement. They pay more.
The main reason is that, in retirement, they have Social Security and required minimum distributions (RMDs) from their tax-deferred investments (IRAs, 401(k)s, etc.). If the tax-deferred investments have significant value, combining the RMDs and Social Security income can result in what is called the “tax torpedo.”
This term refers to the stacking of ordinary income tax and Social Security tax so that additional distributions from your IRA could be taxed at over 40%! Yikes! I do not know about you, but I HATE TAXES (so much that I wrote a book with that exact title, available soon on Amazon), and I would never want to see nearly half of your hard-earned money go to Uncle Sam.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
So, if you are likely to find yourself paying higher taxes in the future, I have some great news. You can reduce your income in retirement to pay less tax!
Taxes in retirement: Social Security
Let us first talk about Social Security tax, which is unique. And keep in mind that before 1983, Social Security benefits were not taxed.
Unfortunately, Social Security has been in trouble because people are living longer, and a big portion of our population is entering into the phase of needing Social Security; therefore, the rules have changed in the past to keep Social Security alive, and they will likely change in the future. It is just simple math.
However, you can avoid paying tax on Social Security. If your income is low enough, you will not have to pay taxes on the money you have worked hard for all your life. If your income is not low enough, let’s see how we can get Social Security tax-free!
Taxes in retirement are determined differently than what you became used to during your accumulation years as you worked your way up the mountain. Now that you are coming down the mountain to live the retirement you want, you have a new set of tax considerations.
This new bracket uses what is called your provisional income. The formula to determine what your provisional income will be: add together half of your Social Security, ordinary income, capital gains and dividends and non-taxable interest. You will take that number to the chart below to determine how much of your benefit is taxable:

So how do we read this chart? If your provisional income is $32,000 or less and you are married and filing jointly, you will find yourself in that 0% tax bracket!
If you find yourself with $32,000-$44,000, then 50% of your benefit will be taxable at your income tax rate. The largest portion of your benefit that could be taxable is 85%. Now do not get scared. It is not an 85% tax rate. Uncle Sam is not that mean.
That number refers merely to the amount of your Social Security that is subject to taxation. So, if your Social Security benefit is $10,000, then 85% of it, or $8,500, is the largest amount that could be taxable at your ordinary income tax rate — for example, a 22% or 24% rate.
So, at most, you would pay around $2,000 in taxes in this example (24% x $8,500). It’s not as bad as you might have thought, but it’s still a lot of money out of your pocket, which I do not like to see.
Keep in mind that the numbers in this table have not changed since 1985. This is what we call a “stealth tax,” which is when the government does not make changes with inflation to benefit you.
Someone in 1985 did not need as much income as you do now and would have found themselves in the lower end of the bracket, whereas more people nowadays find themselves on the higher end.
Come on, Uncle Sam, help us out instead of penalizing us for saving and doing right over the years!
Should you find yourself in this scenario, then you would be in the infamous tax torpedo phase. This is where you could see that 40%-plus tax rate I mentioned. See my chart below for what I call “The Retirees Tax Bracket.”
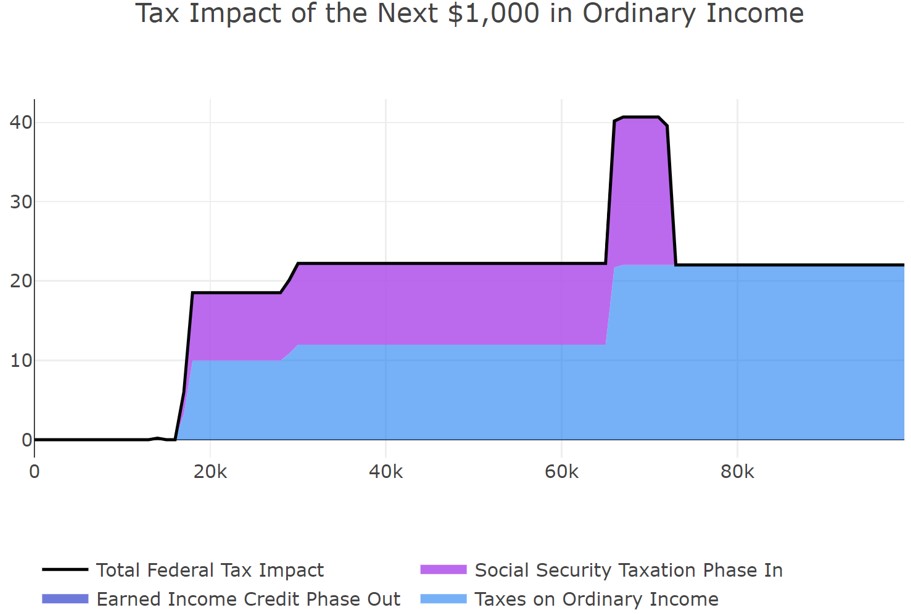
You see that big increase because, in that phase, every dollar you continue to take out keeps pushing your Social Security into that 85% calculation. If you do not push onward, then you avoid that tax! We always plan so we can help our clients stay on the good side of that mountain.
For example, I had a client who was projected to be just over that torpedo. We contributed to an IRA to reduce her income, and that helped her avoid that 40%-plus tax torpedo.
Also, remember at the beginning of this article when I said you will likely not be in a lower tax bracket in retirement? That’s because, as you can see in the above chart, when Social Security becomes taxable, that income could cause you to be around the 20%-plus tax rate.
Keep in mind this could get worse if tax rates increase in the future. (If you think tax rates will be lower with our current debt crisis and spending problems, then you are not in the majority.)
As you can see, it doesn't take a lot of income to trigger Social Security taxes. So, if you can already project that you will be at that point or beyond and are in the 0%-24% bracket now, then you need to take action.
By taking advantage of the current tax environment, you could find yourself in the 0% tax bracket throughout retirement. It is possible with good planning!
Strategies for avoiding the tax torpedo
So how do we get Social Security tax-free or stay on the good side of the tax torpedo?
Roth! Roth! Roth! Roth IRAs and other tax-free vehicles, like health savings accounts (HSAs), loans and life insurance, can prevent you from being forced to pay tax on income you withdraw in the future.
The other important piece here is planning — to determine how to maximize your income in retirement to hit the “sweet spots.” We have many clients who pay 0% taxes in retirement because they allow their income to stay under the standard deduction and keep their provisional income under the 0% limit.
This is really hard to do on your own. I would highly suggest using sophisticated calculators and software to determine all the factors that go into this. I would also suggest working with a professional with expertise in this area. It would likely save you a lot of time, money and mistakes.
Making mistakes in retirement can be costly, and you do not want to find yourself on the wrong side of the tax torpedo in retirement!
Related Content
- When It Comes to Your RMDs, Be Very, Very Afraid!
- Three IRA Mistakes That Are Potentially Costly, Yet Simple to Avoid
- Social Security Optimization If You Save More Than $250,000
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Joe F. Schmitz Jr., CFP®, ChFC®, CKA®, is the founder and CEO of Peak Retirement Planning, Inc., which was named the No. 1 fastest-growing private company in Columbus, Ohio, by Inc. 5000 in 2025. His firm focuses on serving those in the 2% Club by providing the 5 Pillars of Pension Planning. Known as a thought leader in the industry, he is featured in TV news segments and has written three bestselling books: I Hate Taxes (request a free copy), Midwestern Millionaire (request a free copy) and The 2% Club (request a free copy).
Investment Advisory Services and Insurance Services are offered through Peak Retirement Planning, Inc., a Securities and Exchange Commission registered investment adviser able to conduct advisory services where it is registered, exempt or excluded from registration.
-
 3 Smart Ways to Spend Your Retirement Tax Refund
3 Smart Ways to Spend Your Retirement Tax RefundRetirement Taxes With the new "senior bonus" hitting bank accounts this tax season, your retirement refund may be higher than usual. Here's how to reinvest those funds for a financially efficient 2026.
-
 5 Retirement Tax Traps to Watch in 2026
5 Retirement Tax Traps to Watch in 2026Retirement Even in retirement, some income sources can unexpectedly raise your federal and state tax bills. Here's how to avoid costly surprises.
-
 Trump's New Retirement Plan: What You Need to Know
Trump's New Retirement Plan: What You Need to KnowPresident Trump's State of the Union address touched upon several topics, including a new retirement plan for Americans. Here's how it might work.
-
 Buy and Hold … or Buy and Hope? It's Time for a Better Retirement Planning Strategy
Buy and Hold … or Buy and Hope? It's Time for a Better Retirement Planning StrategyOnce you're retired, your focus should shift from maximum growth to strategic preservation and purposeful planning to help safeguard your wealth.
-
 Your Legacy Is More Than Your Money: How to Plan for Values, Not Just Valuables
Your Legacy Is More Than Your Money: How to Plan for Values, Not Just ValuablesLegacy planning integrates your values and stories with legal and tax strategies to ensure your influence benefits loved ones and good causes after you're gone.
-
 Will Real Estate and Private Equity Start to Shine Again in 2026?
Will Real Estate and Private Equity Start to Shine Again in 2026?Real estate, private equity and general partner stakes could benefit from future interest rate cuts. What are the risks and rewards of investing in each?
-
 Your Retirement Age Is Just a Number: Today's Retirement Goal Is 'Work Optional'
Your Retirement Age Is Just a Number: Today's Retirement Goal Is 'Work Optional'Becoming "work optional" is about control — of your time, your choices and your future. This seven-step guide from a financial planner can help you get there.
-
 Have You Fallen Into the High-Earning Trap? This Is How to Escape
Have You Fallen Into the High-Earning Trap? This Is How to EscapeHigh income is a gift, but it can pull you into higher spending, undisciplined investing and overreliance on future earnings. These actionable steps will help you escape the trap.
-
 I'm a Financial Adviser: These 3 Questions Can Help You Navigate a Noisy Year With Financial Clarity
I'm a Financial Adviser: These 3 Questions Can Help You Navigate a Noisy Year With Financial ClarityThe key is to resist focusing only on the markets. Instead, when making financial decisions, think about your values and what matters the most to you.
-
 It's Time to Bust These 3 Long-Term Care Myths (and Face Some Uncomfortable Truths)
It's Time to Bust These 3 Long-Term Care Myths (and Face Some Uncomfortable Truths)None of us wants to think we'll need long-term care when we get older, but the odds are roughly even that we will. Which is all the more reason to understand the realities of LTC and how to pay for it.
-
 Fix Your Mix: How to Derisk Your Portfolio Before Retirement
Fix Your Mix: How to Derisk Your Portfolio Before RetirementIn the run-up to retirement, your asset allocation needs to match your risk tolerance without eliminating potential for growth. Here's how to find the right mix.