When It Comes to Your RMDs, Be Very, Very Afraid!
If you’ve saved heavily in a traditional IRA or 401(k) you may feel great about your retirement savings now, but your required minimum distributions can be frighteningly large in retirement. And the tax bill they generate can be even scarier.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
Editor’s note: This is part two of a seven-part series on retirement tax bombs. It dives more deeply into how required minimum distributions (RMDs) from tax-deferred savings can become a snowballing tax liability in retirement. If you missed the introductory article, you may find it helpful to start here.
For the remaining articles in this series, I’ll use a case study of a couple aged 40 who has saved $500,000 combined in pre-tax retirement accounts. Presumably, this couple is tracking well for a secure retirement. After maxing out their retirement plan contributions, they may not have much cash flow left over and may feel like they’re barely making ends meet. I meet couples like this all time. They aren’t rich, they’re simply good savers doing exactly what conventional wisdom has taught them to do.
The couple keeps making the maximum contribution each year ($20,500 each through age 49, then $27,000 from age 50 to 64, which are the current maximums), and each get a $6,000 employer match. I assume contribution limits rise by 2% annually. The couple’s contributions are in growth allocations that earn an annual 7% return. By the time they retire on their 65th birthdays, their retirement accounts will have grown to an impressive $7.3 million! They’re in great shape, right?
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Snowballing RMD Income
For simplicity, let’s assume they don’t draw down their pre-tax savings early in retirement, so their tax-deferred savings grows to about $11.9 million by age 72, when they must take their first RMD, which is $435,820. The RMD is 100% taxable, at their ordinary income rate, and by itself may put them in a high tax bracket. As you can see in the chart below, the RMD grows to $533,818 at age 75, $739,569 at age 80, $1 million at age 85 and $1.3 million at age 90.
The RMD income dwarfs their annual Social Security income, which I assume at $36,000 each at age 67, with a 2.0% annual cost of living adjustment.
Most people assume their taxable income in retirement will be very low because they’re not working, and will be receiving only Social Security benefits and perhaps some interest and dividend income. But clearly, if you’ve saved a lot in tax-deferred accounts, your RMD income can be frighteningly large. Meet your retirement tax bomb.
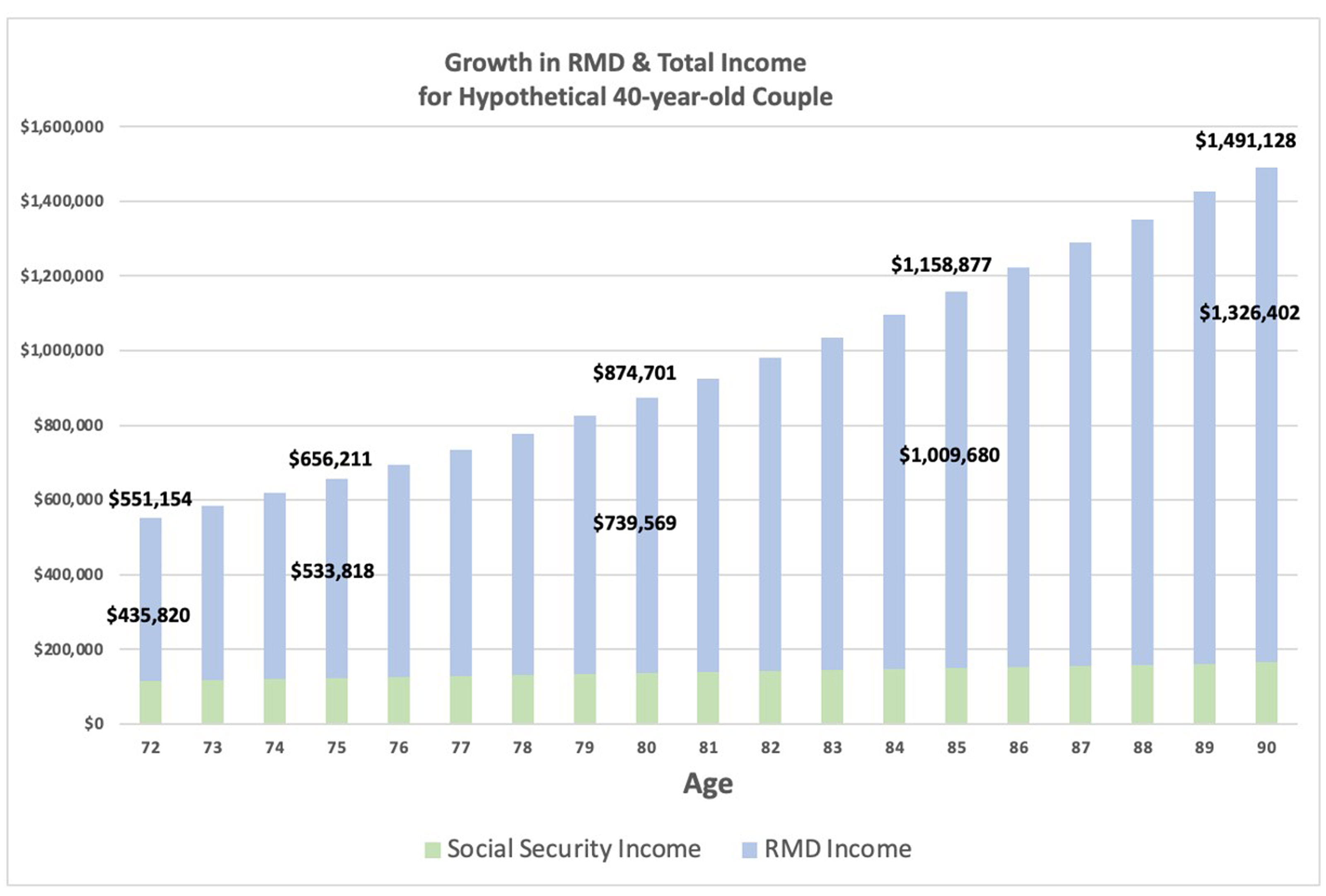
Even though the couple would take $15.6 million in total RMDs from age 72 to 90, their tax liability keeps growing, although at a decreasing rate as the RMDs gets larger. It’s not until age 89 that the RMD exceeds the projected portfolio growth and the tax liability starts shrinking.
Future Tax Rates
As scary as this sounds, think about where future tax rates may be headed. Current tax rates are near historical lows and may be the lowest we'll see for the rest of our lives. Consider solvency issues with Social Security and Medicare, chronic infrastructure issues, exploding deficits, climate change and pandemics. Each of these issues in isolation will require a lot of money to solve. And that doesn't even account for potential policy changes that would tax the wealthy more.
Simply put, paying taxes at today’s low rates may be a bargain compared to deferring, and growing, your tax liabilities into the future.
My next article focuses on problem No. 2: Medicare means testing surcharges.
- Part 1: Is Your Retirement Portfolio a Tax Bomb?
- Part 2: When It Comes to Your RMDs, Be Very, Very Afraid!
- Part 3: RMDs Can Trigger Massive Medicare Means Testing Surcharges
- Part 4: Will Your Kids Inherit a Tax Bomb from You?
- Part 5: How to Defuse a Retirement Tax Bomb, Starting With 1 Simple Move
- Part 6: Using Asset Location to Defuse a Retirement Tax Bomb
- Part 7: Roth Conversions Play Key Role in Defusing a Retirement Tax Bomb
- Bonus article 1: 2 Ways Retirees Can Defuse a Tax Bomb (It’s Not Too Late!)
- Bonus article 2: Can My Pension Trigger a Retirement Tax Bomb?
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

David McClellan is a partner with Forum Financial Management, LP, a Registered Investment Adviser that manages more than $7 billion in client assets. He is also VP and Head of Wealth Management Solutions at AiVante, a technology company that uses artificial intelligence to predict lifetime medical expenses. Previously David spent nearly 15 years in executive roles with Morningstar (where he designed retirement income planning software) and Pershing. David is based in Austin, Texas, but works with clients nationwide. His practice focuses on financial life coaching and retirement planning. He frequently helps clients assess and defuse retirement tax bombs.
-
 Quiz: Do You Know How to Avoid the "Medigap Trap?"
Quiz: Do You Know How to Avoid the "Medigap Trap?"Quiz Test your basic knowledge of the "Medigap Trap" in our quick quiz.
-
 5 Top Tax-Efficient Mutual Funds for Smarter Investing
5 Top Tax-Efficient Mutual Funds for Smarter InvestingMutual funds are many things, but "tax-friendly" usually isn't one of them. These are the exceptions.
-
 AI Sparks Existential Crisis for Software Stocks
AI Sparks Existential Crisis for Software StocksThe Kiplinger Letter Fears that SaaS subscription software could be rendered obsolete by artificial intelligence make investors jittery.
-
 Social Security Break-Even Math Is Helpful, But Don't Let It Dictate When You'll File
Social Security Break-Even Math Is Helpful, But Don't Let It Dictate When You'll FileYour Social Security break-even age tells you how long you'd need to live for delaying to pay off, but shouldn't be the sole basis for deciding when to claim.
-
 I'm an Opportunity Zone Pro: This Is How to Deliver Roth-Like Tax-Free Growth (Without Contribution Limits)
I'm an Opportunity Zone Pro: This Is How to Deliver Roth-Like Tax-Free Growth (Without Contribution Limits)Investors who combine Roth IRAs, the gold standard of tax-free savings, with qualified opportunity funds could enjoy decades of tax-free growth.
-
 One of the Most Powerful Wealth-Building Moves a Woman Can Make: A Midcareer Pivot
One of the Most Powerful Wealth-Building Moves a Woman Can Make: A Midcareer PivotIf it feels like you can't sustain what you're doing for the next 20 years, it's time for an honest look at what's draining you and what energizes you.
-
 I'm a Wealth Adviser Obsessed With Mahjong: Here Are 8 Ways It Can Teach Us How to Manage Our Money
I'm a Wealth Adviser Obsessed With Mahjong: Here Are 8 Ways It Can Teach Us How to Manage Our MoneyThis increasingly popular Chinese game can teach us not only how to help manage our money but also how important it is to connect with other people.
-
 Looking for a Financial Book That Won't Put Your Young Adult to Sleep? This One Makes 'Cents'
Looking for a Financial Book That Won't Put Your Young Adult to Sleep? This One Makes 'Cents'"Wealth Your Way" by Cosmo DeStefano offers a highly accessible guide for young adults and their parents on building wealth through simple, consistent habits.
-
 Global Uncertainty Has Investors Running Scared: This Is How Advisers Can Reassure Them
Global Uncertainty Has Investors Running Scared: This Is How Advisers Can Reassure ThemHow can advisers reassure clients nervous about their plans in an increasingly complex and rapidly changing world? This conversational framework provides the key.
-
 I'm a Real Estate Investing Pro: This Is How to Use 1031 Exchanges to Scale Up Your Real Estate Empire
I'm a Real Estate Investing Pro: This Is How to Use 1031 Exchanges to Scale Up Your Real Estate EmpireSmall rental properties can be excellent investments, but you can use 1031 exchanges to transition to commercial real estate for bigger wealth-building.
-
 Should You Jump on the Roth Conversion Bandwagon? A Financial Adviser Weighs In
Should You Jump on the Roth Conversion Bandwagon? A Financial Adviser Weighs InRoth conversions are all the rage, but what works well for one household can cause financial strain for another. This is what you should consider before moving ahead.