Disrupters Are Driving the Car Market
I was not a Tesla believer years ago, but I am now. Tesla's future looks pretty spectacular, and its stock price has lately become more attractive.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
When I was 9, my grandfather gave me a present: my first share of stock. It was a gorgeous, embossed certificate issued by the Ford Motor (F), which had just gone public on January 18, 1956, at $64.50 a share.
In 1988, I decided to sell my share, which after splits had become many shares worth $828. Selling at the time turned out to be a good idea. Ford shares peaked in 1999.
But don’t count Ford out. The drop in revenues from the pandemic was not as bad as expected, and over the past 12 months, the stock has returned 143%; General Motors (GM) has returned 162%.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Ford and GM, two stodgy companies that have been selling pretty much the same product for more than a century, have felt the shock of an earthshaking disruption of their industry. It's a case of respond or die, and the two companies have responded, though a bit late.
Disruptive innovation is a term coined in 1995 by Harvard Business School professor Clayton Christensen. Most people use the shorthand disruption to mean a general shake-up in an industry. But Christensen, who died last year, had a more precise definition: "a process whereby a smaller company with fewer resources is able to successfully challenge established incumbent businesses."
While the incumbents are focused on gradually improving their products to satisfy traditional customers, disrupters target "overlooked segments, gaining a foothold," Christensen wrote.
Incumbents ignore disrupters because those segments are small or unprofitable. The disrupters then expand their offerings, "delivering the performance that incumbents' mainstream customers require, while preserving the advantages that drove their early success." When mainstream customers start adopting the disrupters' products "in volume," you've got real disruption.
Tesla: A Model Disrupter
A model disrupter. An upstart called Tesla Motors, now just Tesla (TSLA), fits the Christensen model. The company was launched in 2003, released its first plug-in electric car five years later, and went public two years after that. Elon Musk took his earnings as cofounder of PayPal Holdings (PYPL) and became an early investor in Tesla; in 2008, he became CEO.
In 2015, when Christensen’s article from which I'm quoting appeared in the Harvard Business Review, Tesla had two models and it sold 50,000 cars. Sales doubled in two years and reached 500,000 in 2020; this year, the forecast is 800,000 vehicles.
Tesla is by far the largest global electric vehicle maker, manufacturing four models, including one with a list price of only $40,120. It's working on a beautiful long-haul truck. Holding Tesla back from even more sales this year is a pandemic-induced shortage of microchips, which should be temporary.
The incumbents have responded. Last year, Ford said it would invest $11.5 billion in electric vehicles through 2022, producing a zero-emissions Mustang and F-150 truck. In January, GM announced it would phase out petroleum-fueled vehicles and sell only cars and trucks that produce zero emissions.
I was not a Tesla believer years ago, but I am now. Tesla is still small ($32 billion in revenues last year, compared with GM's $122 billion) and unprofitable. An investment in Bitcoin and sales of regulatory credits to internal-combustion-engine carmakers saved Tesla from showing a loss in the most recent quarter.
Stocks, however, are priced according to expectations, not history, and Tesla's future looks spectacular. In late 2019, Teslas started rolling out of a $2 billion factory in Shanghai, and in April the company announced a $1 billion factory in Austin, Texas.
Musk forecasts that Tesla's U.S. market share will rise from 2% today to 10% in 2025, and analysts at Morgan Stanley project that the company's manufacturing capacity will reach 5.5 million vehicles by 2030. That compares favorably with GM's 6.8 million in 2020.
Tesla's stock price has become more attractive lately, dropping more than 20% from its January peak, partly because of the chip shortage. Its market capitalization (shares outstanding times price) is $647 billion, or nearly twice as much as GM, Ford and Toyota Motor (TM) combined. In fact, Tesla is the seventh-largest U.S. company by market cap, after five tech giants and Berkshire Hathaway (BRK.B); it's bigger than Walmart (WMT) and JPMorgan Chase (JPM).
Is this crazy?
I don't think so. The global auto market is estimated to grow to $9 trillion by 2030.
11 More Automotive Innovators
Tech is the ignition. Tesla is not the only vehicle disrupter. Technology is front and center in the sector. Small, innovative companies abound, most of them still private. But there are good stocks to buy. One of the largest is the dominant ride-hailing company, Uber (UBER), with a market cap of about $90 billion.
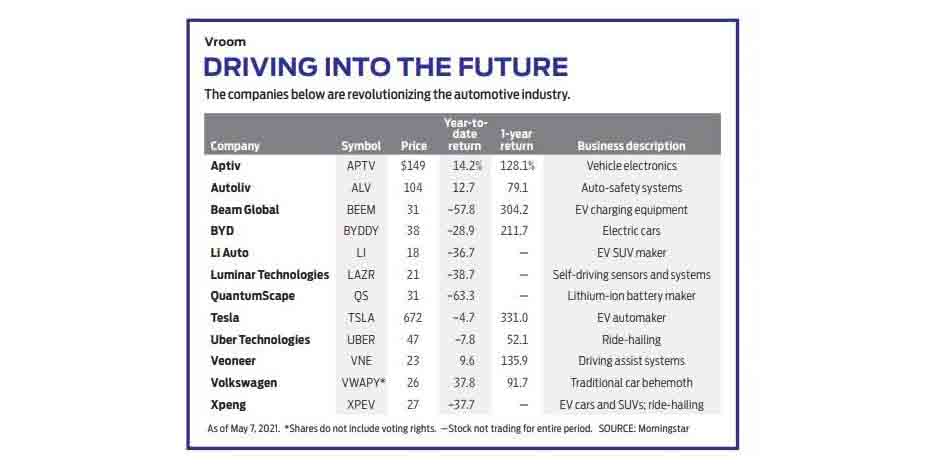
Veoneer (VNE) is a Swedish company that makes automobile-mounted cameras, systems that assist night driving and other navigation electronics. Sales were hit last year by the pandemic, and the stock trades at less than half its 2018 high.
Another attractive Swedish firm, Autoliv (ALV), makes auto-safety systems for the global auto industry. Autoliv has been consistently profitable, with a stock that's up by more than half this year. Aptiv (APTV), an Irish maker of sophisticated vehicle electronics, is also highly profitable, with a $38 billion market cap.
Another company with substantial sales and earnings and a commitment to EVs is BYD (BYDDY), based in Shenzhen, China, with a market cap of $60 billion. BYD (an acronym for “Build Your Dreams”) started as a battery maker and now manufactures electric and internal-combustion vehicles; some of its EVs sell for as little as $9,000. Nearly all of Shenzhen’s 20,000 taxis are BYDs. Part of the appeal of BYD: The stock is down 46% since February, despite consistently rising revenues.
China is the largest market for EVs, with 1.2 million sales last year. Two other Chinese manufacturers to note are Li Auto (LI), whose niche is SUVs, and the larger XPeng (XPEV), which makes SUVs and a four-door sport sedan; Xpeng is also in the ride-hailing business. Both stocks are well priced, having fallen by half in less than six months.
More risky but worth consideration are some early-stage auto-tech firms. Luminar Technologies (LAZR) makes sensors and software that enable autonomous driving. Luminar had only $14 million in sales last year, but its prospects have earned it a market cap of $7 billion.
QuantumScape (QS) is a lithium-ion battery maker with no sales in 2020 but a market cap of $12 billion. Beam Global (BEEM), with a market cap of just $276 million, specializes in clean-energy charging equipment for EVs; one of its products uses solar power.
If you prefer a traditional automaker stock, my top choice is Volkswagen (VWAGY), with a dozen brands from seven European countries, including Audi, Bentley and Porsche, plus the truck and bus companies Scania and MAN. VW sold only half as many EVs as Tesla last year, but the demand in Europe is intense, as it will soon be in the U.S.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

-
 Dow Dives 521 Points as Goldman, AmEx Slide: Stock Market Today
Dow Dives 521 Points as Goldman, AmEx Slide: Stock Market TodayNews of Block's massive layoffs exacerbated AI worries across the financial sector.
-
 8 Boring Habits That Will Make You Rich in Retirement
8 Boring Habits That Will Make You Rich in RetirementThese mundane activities won't make you the life of the party, but they will set you up for a rich retirement. Discover the 8 boring habits that build real wealth.
-
 QUIZ: Are You Ready To Retire At 55?
QUIZ: Are You Ready To Retire At 55?Quiz Are you in a good position to retire at 55? Find out with this quick quiz.
-
 Why I Trust These Trillion-Dollar Stocks
Why I Trust These Trillion-Dollar StocksThe top-heavy nature of the S&P 500 should make any investor nervous, but there's still plenty to like in these trillion-dollar stocks.
-
 Elon Musk's $1 Trillion Pay Package Passes: What's at Stake for Tesla Stock
Elon Musk's $1 Trillion Pay Package Passes: What's at Stake for Tesla StockMore than 75% of Tesla shareholders voted to approve a massive pay package for CEO Elon Musk. Here's what it means for the Mag 7 stock.
-
 The Most Tax-Friendly States for Investing in 2025 (Hint: There Are Two)
The Most Tax-Friendly States for Investing in 2025 (Hint: There Are Two)State Taxes Living in one of these places could lower your 2025 investment taxes — especially if you invest in real estate.
-
 The Riskiest S&P 500 Stocks Right Now
The Riskiest S&P 500 Stocks Right NowBuyer beware: These are five of the riskiest stocks in the S&P 500 at the moment, based on one measure of volatility.
-
 Stock Market Today: Wall Street Is Standing By
Stock Market Today: Wall Street Is Standing ByThe waiting is the hardest part with trade war truce talks underway and inflation data on the way.
-
 Stock Market Today: Stocks Stable as Inflation, Tariff Fears Ebb
Stock Market Today: Stocks Stable as Inflation, Tariff Fears EbbConstructive trade war talks and improving consumer expectations are a healthy combination for financial markets.
-
 Stock Market Today: Good Feelings and Solid Data Lift Stocks
Stock Market Today: Good Feelings and Solid Data Lift StocksResilience and de-escalation defined another generally positive day for financial markets.
-
 Stock Market Today: Tesla Drags on Stocks Amid Musk-Trump Feud
Stock Market Today: Tesla Drags on Stocks Amid Musk-Trump FeudSentiment has soured between President Trump and his once-loyal ally, Tesla CEO Elon Musk.