Dollar-Cost Averaging Into Stocks: How Does DCA Investing Work?
A brief primer on dollar-cost averaging into stocks, the popular set-it-and-forget-it investing method.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
Dollar-cost averaging (DCA) is one of the most important concepts an individual investor can master.
Fortunately, it's also one of the easiest.
The idea of dollar-cost averaging is to invest your dollars in a stock, exchange-traded fund (ETF) or other security in regular, equal portions over time.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Sure, you could invest your cash in a single lump sum, but how do you know you're getting the best price? (Remember: The idea is to buy low.)
In the short term, many stock movements can be random, and even the pros are more likely to fail than succeed when trying to precisely time the market.
Dollar-cost averaging doesn't guarantee you the lowest cost basis on your investments. It can, however, produce a lower average cost basis over a longer period of time than lump-sum investing.
And, again, it's easy to do.
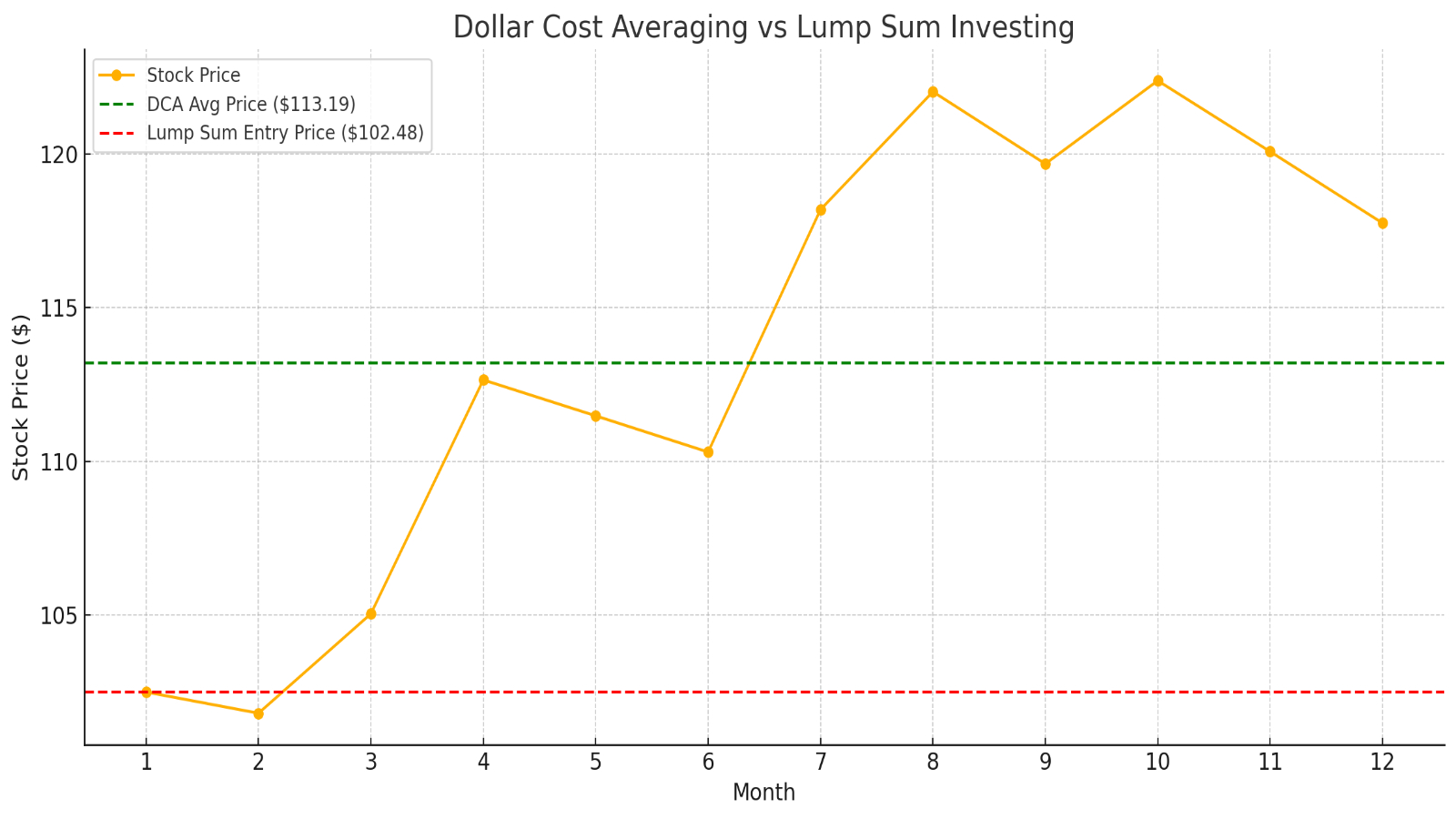
How dollar-cost averaging works
If you have a 401(k) or similar plan where you automatically invest a percentage of every paycheck in a retirement plan, guess what? You are already dollar-cost averaging.
That's because every pay period, you're investing the same amount of cash like clockwork.
But say you want to do this in an IRA or brokerage account. Here's an example of how this would work with an individual stock.
You have $10,000 to invest in, say, grocery chain Kroger (KR). You effectively have two options:
1.) Make a lump-sum investment of $10,000. If shares in the supermarket chain decline soon after you make your investment, however, you might kick yourself over your poor timing.
2.) Dollar-cost average, investing the $10,000 gradually and at regular intervals. For instance, you might purchase $833.33 worth of KR stock every month for 12 months.
The beauty of dollar-cost averaging is that if Kroger stock does indeed decline over that period of time, you'll buy KR shares at a lower cost. Thus, you'll get more shares for your $833.33, too.
Here's how dollar-cost averaging with KR would've looked across 2019, assuming you had bought at the closing price of each month:
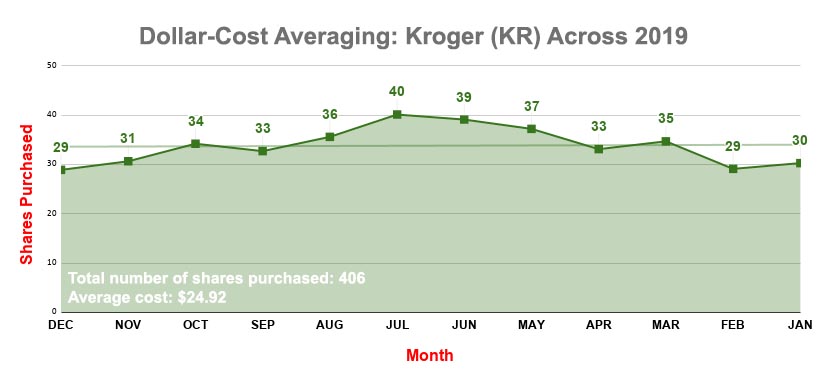
In short, DCA lets an investor automatically buy more shares in a company when they're cheaper, and fewer shares when they're more expensive.
Nothing's a guarantee, of course
As with everything in investing, DCA is not without its detractors. Dollar-cost averaging can underperform lump-sum investing at times.
But while systematic investing does not guarantee a profit or protect against loss, it can lift a psychological brick or two off your shoulders.
With DCA, you don't need to agonize over whether you should buy right now, or wait for earnings, or wait for a market dip. You just implement the system and keep yourself updated on the stock over time.
Investors also need to consider whether they have the stomach to keep buying when share prices are falling or the stock market is selling off.
Dollar-cost averaging doesn't mean to throw good money after bad if the company's narrative has changed considerably. But it does mean being consistent through short-term ups and downs.
That said, DCA can be a good strategy for long-term investors who just want to set it and forget it.
Related Content
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Dan Burrows is Kiplinger's senior investing writer, having joined the publication full time in 2016.
A long-time financial journalist, Dan is a veteran of MarketWatch, CBS MoneyWatch, SmartMoney, InvestorPlace, DailyFinance and other tier 1 national publications. He has written for The Wall Street Journal, Bloomberg and Consumer Reports and his stories have appeared in the New York Daily News, the San Jose Mercury News and Investor's Business Daily, among many other outlets. As a senior writer at AOL's DailyFinance, Dan reported market news from the floor of the New York Stock Exchange.
Once upon a time – before his days as a financial reporter and assistant financial editor at legendary fashion trade paper Women's Wear Daily – Dan worked for Spy magazine, scribbled away at Time Inc. and contributed to Maxim magazine back when lad mags were a thing. He's also written for Esquire magazine's Dubious Achievements Awards.
In his current role at Kiplinger, Dan writes about markets and macroeconomics.
Dan holds a bachelor's degree from Oberlin College and a master's degree from Columbia University.
Disclosure: Dan does not trade individual stocks or securities. He is eternally long the U.S equity market, primarily through tax-advantaged accounts.
-
 Dow Adds 1,206 Points to Top 50,000: Stock Market Today
Dow Adds 1,206 Points to Top 50,000: Stock Market TodayThe S&P 500 and Nasdaq also had strong finishes to a volatile week, with beaten-down tech stocks outperforming.
-
 Ask the Tax Editor: Federal Income Tax Deductions
Ask the Tax Editor: Federal Income Tax DeductionsAsk the Editor In this week's Ask the Editor Q&A, Joy Taylor answers questions on federal income tax deductions
-
 States With No-Fault Car Insurance Laws (and How No-Fault Car Insurance Works)
States With No-Fault Car Insurance Laws (and How No-Fault Car Insurance Works)A breakdown of the confusing rules around no-fault car insurance in every state where it exists.
-
 Dow Adds 1,206 Points to Top 50,000: Stock Market Today
Dow Adds 1,206 Points to Top 50,000: Stock Market TodayThe S&P 500 and Nasdaq also had strong finishes to a volatile week, with beaten-down tech stocks outperforming.
-
 The Best Precious Metals ETFs to Buy in 2026
The Best Precious Metals ETFs to Buy in 2026Precious metals ETFs provide a hedge against monetary debasement and exposure to industrial-related tailwinds from emerging markets.
-
 For the 2% Club, the Guardrails Approach and the 4% Rule Do Not Work: Here's What Works Instead
For the 2% Club, the Guardrails Approach and the 4% Rule Do Not Work: Here's What Works InsteadFor retirees with a pension, traditional withdrawal rules could be too restrictive. You need a tailored income plan that is much more flexible and realistic.
-
 Retiring Next Year? Now Is the Time to Start Designing What Your Retirement Will Look Like
Retiring Next Year? Now Is the Time to Start Designing What Your Retirement Will Look LikeThis is when you should be shifting your focus from growing your portfolio to designing an income and tax strategy that aligns your resources with your purpose.
-
 I'm a Financial Planner: This Layered Approach for Your Retirement Money Can Help Lower Your Stress
I'm a Financial Planner: This Layered Approach for Your Retirement Money Can Help Lower Your StressTo be confident about retirement, consider building a safety net by dividing assets into distinct layers and establishing a regular review process. Here's how.
-
 Stocks Sink With Alphabet, Bitcoin: Stock Market Today
Stocks Sink With Alphabet, Bitcoin: Stock Market TodayA dismal round of jobs data did little to lift sentiment on Thursday.
-
 The 4 Estate Planning Documents Every High-Net-Worth Family Needs (Not Just a Will)
The 4 Estate Planning Documents Every High-Net-Worth Family Needs (Not Just a Will)The key to successful estate planning for HNW families isn't just drafting these four documents, but ensuring they're current and immediately accessible.
-
 Love and Legacy: What Couples Rarely Talk About (But Should)
Love and Legacy: What Couples Rarely Talk About (But Should)Couples who talk openly about finances, including estate planning, are more likely to head into retirement joyfully. How can you get the conversation going?