What Makes a Value Stock?
Some of the distinction between growth and value is in the eye of the beholder.

Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
What is a value stock, really? “I know it when I see it,” says Robert Waid, who heads up the index business at investment consulting firm Wilshire Associates. “It’s like the difference between pornography and art.”
All kidding aside, Waid admits that determining what constitutes a bargain stock—and its counterpart, a growth stock—is complicated. In simplest terms, a value stock is one that is cheap in relation to such basic measures of corporate performance as earnings, sales, book value and cash flow. Examples of what are commonly viewed as value stocks are Citicorp (C), ExxonMobil (XOM)and JPMorgan Chase (JPM). Growth companies, by contrast, boast rapidly expanding profits and revenues, and their stocks typically command high valuations. Think Amazon.com (AMZN) and Facebook (FB).
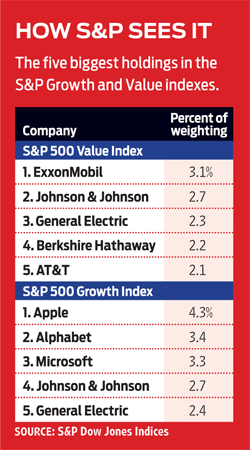
Several firms, including Wilshire and S&P Dow Jones Indices, maintain indexes that divide the stock market into growth and value segments. They do so by ranking stocks on a variety of factors, such as profit and sales growth, price-earnings ratios, and so on. Financial and energy stocks tend to fall in the value camp; technology and health care land in the growth group./p>
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
But there’s plenty of room for interpretation. Are Alphabet (GOOGL) (the former Google) and Microsoft (MSFT) growth stocks or value stocks? Apparently, they are both. Dodge & Cox Stock (DODGX), a classic value fund, and Harbor Capital Appreciation (HACAX), which focuses on fast growers, own both stocks.
As once-small firms turn into behemoths, growth companies often turn into value stocks. That was certainly the case with such former technology luminaries as Cisco Systems, EMC and Intel. And that may be happening today with Apple (AAPL) and biotech giant Gilead Sciences (GILD). At its June 30 close of $96, Apple was selling for 11 times estimated year-ahead earnings, and Gilead, at $83, was trading for a seemingly absurd 7 times forecast profits. The overall U.S. stock market sells for 17 times estimated earnings. And although earnings growth at both companies has stalled, index sponsors for the most part still consider both firms to be growth stocks.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Nellie joined Kiplinger in August 2011 after a seven-year stint in Hong Kong. There, she worked for the Wall Street Journal Asia, where as lifestyle editor, she launched and edited Scene Asia, an online guide to food, wine, entertainment and the arts in Asia. Prior to that, she was an editor at Weekend Journal, the Friday lifestyle section of the Wall Street Journal Asia. Kiplinger isn't Nellie's first foray into personal finance: She has also worked at SmartMoney (rising from fact-checker to senior writer), and she was a senior editor at Money.
-
 Farmers Brace for Another Rough Year
Farmers Brace for Another Rough YearThe Kiplinger Letter The agriculture sector has been plagued by low commodity prices and is facing an uncertain trade outlook.
-
 Stocks Drop as Iran Worries Ramp Up: Stock Market Today
Stocks Drop as Iran Worries Ramp Up: Stock Market TodayPresident Trump said he will decide within the next 10 days whether or not the U.S. will launch military strikes against Iran.
-
 Over 65? Here's What the New $6K Senior Tax Deduction Means for Medicare IRMAA
Over 65? Here's What the New $6K Senior Tax Deduction Means for Medicare IRMAATax Breaks A new tax deduction for people over age 65 has some thinking about Medicare premiums and MAGI strategy.
-
 If You'd Put $1,000 Into AMD Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have Today
If You'd Put $1,000 Into AMD Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have TodayAdvanced Micro Devices stock is soaring thanks to AI, but as a buy-and-hold bet, it's been a market laggard.
-
 If You'd Put $1,000 Into UPS Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have Today
If You'd Put $1,000 Into UPS Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have TodayUnited Parcel Service stock has been a massive long-term laggard.
-
 Stocks See First Back-to-Back Losses of 2026: Stock Market Today
Stocks See First Back-to-Back Losses of 2026: Stock Market TodayRising geopolitical worries and a continued sell off in financial stocks kept pressure on the main indexes on Wednesday.
-
 If You'd Put $1,000 Into Lowe's Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have Today
If You'd Put $1,000 Into Lowe's Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have TodayLowe's stock has delivered disappointing returns recently, but it's been a great holding for truly patient investors.
-
 If You'd Put $1,000 Into 3M Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have Today
If You'd Put $1,000 Into 3M Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have TodayMMM stock has been a pit of despair for truly long-term shareholders.
-
 If You'd Put $1,000 Into Coca-Cola Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have Today
If You'd Put $1,000 Into Coca-Cola Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You'd Have TodayEven with its reliable dividend growth and generous stock buybacks, Coca-Cola has underperformed the broad market in the long term.
-
 If You Put $1,000 into Qualcomm Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You Would Have Today
If You Put $1,000 into Qualcomm Stock 20 Years Ago, Here's What You Would Have TodayQualcomm stock has been a big disappointment for truly long-term investors.
-
 Why I Trust These Trillion-Dollar Stocks
Why I Trust These Trillion-Dollar StocksThe top-heavy nature of the S&P 500 should make any investor nervous, but there's still plenty to like in these trillion-dollar stocks.

