Is a Recession on the Way?
The recent dip in long-term bond yields below short-term yields isn't cause for panic.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
Market watchers broke into a collective sweat recently when the yield on 10-year Treasuries sank below the 3-month T-bill yield. When yields on short-term debt exceed those on longer-term bonds, the yield curve—a representation of interest rates on bonds of varying maturities—is said to be inverted. A little perspiration is understandable: An inverted yield curve has preceded each of the past seven recessions, dating back to the mid 1960s.
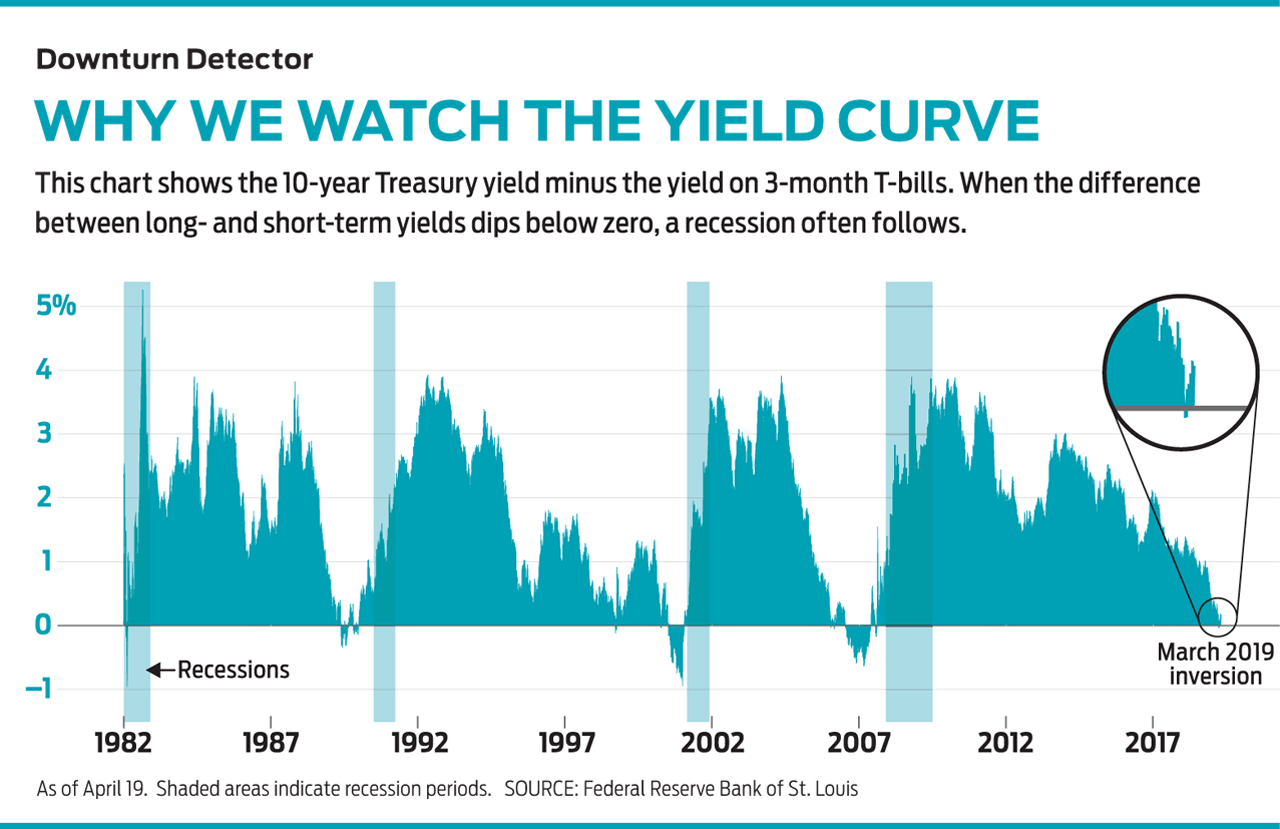
An inversion is considered a recession indicator because although short-term rates are driven by current Federal Reserve policy, longer-term rates reflect bond investors’ expectations for inflation and future economic growth. When investors believe that the economy will weaken, they tend to pile into the safe haven of longer-term Treasuries, locking in higher rates while they can. In doing so, they bid up the price of long-maturity bonds, driving down yields (bond prices and yields move in opposite directions). A yield curve inversion is an extreme, and rare, no-confidence vote.
As with any economic bellwether, the yield curve isn’t foolproof. Although all recessions since the ’60s have followed inversions, not all inversions have led to recessions. And there is little predictability as to when a recession will hit or how long it will last. Since 1968, the time between the inversion and eventual recession has ranged from five to 16 months.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Moreover, March’s inversion wasn’t severe (a difference of only a few hundredths of a percentage point) or long-lasting (it has since flipped back). Should the long end dip more than 0.5 percentage point below the short end, it would be cause for greater concern, says LPL senior market strategist Ryan Detrick.
Whether the recent inversion is a blip or a harbinger of recession remains to be seen. Regardless, investors should consider it a sign that things are closer to the end than the beginning of the economic cycle, says Sam Stovall, chief investment strategist at research firm CFRA. “By July, it will have been the longest economic expansion in history. Things don’t last forever, right?” he says.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Ryan joined Kiplinger in the fall of 2013. He wrote and fact-checked stories that appeared in Kiplinger's Personal Finance magazine and on Kiplinger.com. He previously interned for the CBS Evening News investigative team and worked as a copy editor and features columnist at the GW Hatchet. He holds a BA in English and creative writing from George Washington University.
-
 Nasdaq Leads a Rocky Risk-On Rally: Stock Market Today
Nasdaq Leads a Rocky Risk-On Rally: Stock Market TodayAnother worrying bout of late-session weakness couldn't take down the main equity indexes on Wednesday.
-
 Quiz: Do You Know How to Avoid the "Medigap Trap?"
Quiz: Do You Know How to Avoid the "Medigap Trap?"Quiz Test your basic knowledge of the "Medigap Trap" in our quick quiz.
-
 5 Top Tax-Efficient Mutual Funds for Smarter Investing
5 Top Tax-Efficient Mutual Funds for Smarter InvestingMutual funds are many things, but "tax-friendly" usually isn't one of them. These are the exceptions.
-
 Big Change Coming to the Federal Reserve
Big Change Coming to the Federal ReserveThe Lette A new chairman of the Federal Reserve has been named. What will this mean for the economy?
-
 Job Growth Sizzled to Start the Year. Here's Why It's Unlikely to Impact Interest Rates
Job Growth Sizzled to Start the Year. Here's Why It's Unlikely to Impact Interest RatesThe January jobs report came in much stronger than expected and the unemployment rate ticked lower to start 2026, easing worries about a slowing labor market.
-
 Why the Next Fed Chair Decision May Be the Most Consequential in Decades
Why the Next Fed Chair Decision May Be the Most Consequential in DecadesKevin Warsh, Trump's Federal Reserve chair nominee, faces a delicate balancing act, both political and economic.
-
 The New Fed Chair Was Announced: What You Need to Know
The New Fed Chair Was Announced: What You Need to KnowPresident Donald Trump announced Kevin Warsh as his selection for the next chair of the Federal Reserve, who will replace Jerome Powell.
-
 The U.S. Economy Will Gain Steam This Year
The U.S. Economy Will Gain Steam This YearThe Kiplinger Letter The Letter editors review the projected pace of the economy for 2026. Bigger tax refunds and resilient consumers will keep the economy humming in 2026.
-
 January Fed Meeting: Updates and Commentary
January Fed Meeting: Updates and CommentaryThe January Fed meeting marked the first central bank gathering of 2026, with Fed Chair Powell & Co. voting to keep interest rates unchanged.
-
 Trump Reshapes Foreign Policy
Trump Reshapes Foreign PolicyThe Kiplinger Letter The President starts the new year by putting allies and adversaries on notice.
-
 Congress Set for Busy Winter
Congress Set for Busy WinterThe Kiplinger Letter The Letter editors review the bills Congress will decide on this year. The government funding bill is paramount, but other issues vie for lawmakers’ attention.