How the Social Security Earnings Test May Affect Your Retirement
If you start taking Social Security benefits before your full retirement age and decide to continue working, you need to understand how the earnings test works.


Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
More than half of Americans surveyed by Voya Financial plan to work in retirement. If you share that plan, you may assume that you can easily combine paid employment with other sources of retirement income, such as your retirement savings and Social Security.
However, if you claim Social Security before your full retirement age — which is based on your year of birth — your benefits may be reduced through a mechanism known as the Social Security earnings test. Essentially, this rule limits your benefits if your paid employment earnings exceed certain thresholds.
The good news is that once you reach full retirement age, the benefit amounts that were withheld due to the earnings test will be returned to you in future Social Security payments. However, that doesn’t help when you are trying to balance your budget during the early years of retirement.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
How the earnings test works
The impact of the earnings test on your benefit can be broken down into three distinct phases. Each phase is based on your current age relative to your full retirement age.
- Stage 1: You will not reach full retirement age in 2021: In this stage, you can earn as much as $18,960 a year from employment without affecting your Social Security benefits. There will be a $1 reduction in Social Security payments for every $2 of earnings over the $18,960 limit. In the event of a reduction, Social Security withholds benefits in the form of whole payments at the beginning of the year. If Social Security withholds too much, that means money will be refunded in the next calendar year.
- Stage 2: You will reach your full retirement age in 2021 If you will reach your full retirement age during 2021, the earnings test is much less restrictive. You can earn as much as $50,520 a year from employment without affecting your benefit. There will be $1 reduction for every $3 of earnings over the $50,520 limit.
- Stage 3: You reached your full retirement age before 2021: If you have already reached your full retirement age before 2021, the earnings test doesn’t apply to your earnings. You are free to earn as much as you want while receiving your full benefit.
Special Rule: A special rule exists for filers that fall into phase 1 and 2 who retire from employment mid-year. Regardless of your earnings, if you stop receiving employment income once you collect Social Security, you can collect your entire benefit without reduction due to the excess earnings test.
Social Security claiming primer
The amount of your Social Security benefit depends on your earnings history and your age. Social Security benchmarks all benefits around the concept of full retirement age, which for those born between 1943 and 1960 is between ages 66 to 67.
At full retirement age you receive what is known as your full benefit or primary insurance amount (PIA). If you claim Social Security before your full retirement age, your benefit is reduced. Similarly, if you claim after your full retirement age, your benefit is increased.
The earliest you can claim Social Security is age 62; the latest you can claim to receive the maximum potential benefit is age 70.
Social Security Full Retirement Age Table
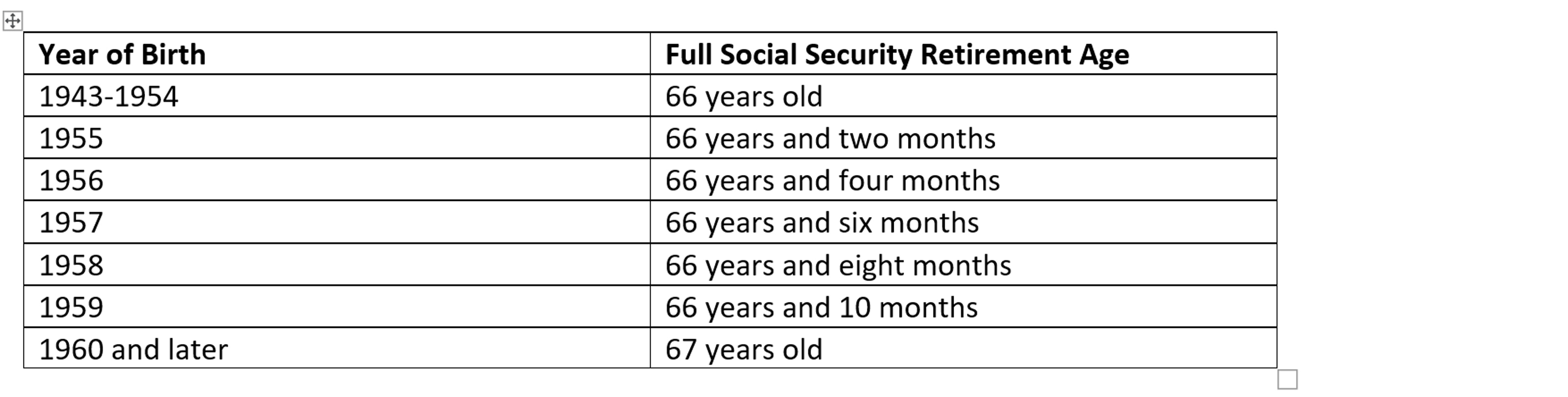
Source: U.S. Social Security Administration
Managing employment and Social Security benefits
Ultimately, the Social Security earnings test does not affect the benefit you receive over the course of your retirement because Social Security will make up any benefit reductions later when you reach full retirement age.
However, this isn’t much comfort when you’re trying to balance your budget in early retirement. That’s why it’s critical to understand the earnings test and weigh all of your possible options when making your Social Security filing decision.
Amy Buttell contributed to this article.
Advisory services offered through J.W. Cole Advisors, Inc & Blue Financial are unaffiliated entities. No information provided is intended as a solicitation to buy or sell any security. Blue Financial is an independent financial services firm helping individuals create retirement strategies using a variety of investment and insurance products to custom suit their needs and objectives. This material has been prepared for informational and educational purposes only. It is not intended to provide, and should not be relied upon for, accounting, legal, tax, or investment advice.
Licensed Insurance Professional. The licensed professional can provide information, but not advice related to social security benefits. The licensed professional may be able to identify potential retirement income gaps and may introduce insurance products, such as an annuity, as a potential solution. For more information, contact the Social Security Administration office, or visit www.ssa.gov. 20988 - 2021/5/3
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

Austin Powell is a wealth adviser at Blue Financial. He has a bachelor’s in business administration from North Carolina State University, where he was also an All-ACC tennis player. He has earned the prestigious CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER™ certification in addition to being a National Social Security Advisor (NSSA®). He has a Series 65 securities license and a life & health insurance license. As a fiduciary, he operates with full transparency and does what is in the best interest of his clients.
-
 Quiz: Do You Know How to Avoid the "Medigap Trap?"
Quiz: Do You Know How to Avoid the "Medigap Trap?"Quiz Test your basic knowledge of the "Medigap Trap" in our quick quiz.
-
 5 Top Tax-Efficient Mutual Funds for Smarter Investing
5 Top Tax-Efficient Mutual Funds for Smarter InvestingMutual funds are many things, but "tax-friendly" usually isn't one of them. These are the exceptions.
-
 AI Sparks Existential Crisis for Software Stocks
AI Sparks Existential Crisis for Software StocksThe Kiplinger Letter Fears that SaaS subscription software could be rendered obsolete by artificial intelligence make investors jittery.
-
 Social Security Break-Even Math Is Helpful, But Don't Let It Dictate When You'll File
Social Security Break-Even Math Is Helpful, But Don't Let It Dictate When You'll FileYour Social Security break-even age tells you how long you'd need to live for delaying to pay off, but shouldn't be the sole basis for deciding when to claim.
-
 I'm an Opportunity Zone Pro: This Is How to Deliver Roth-Like Tax-Free Growth (Without Contribution Limits)
I'm an Opportunity Zone Pro: This Is How to Deliver Roth-Like Tax-Free Growth (Without Contribution Limits)Investors who combine Roth IRAs, the gold standard of tax-free savings, with qualified opportunity funds could enjoy decades of tax-free growth.
-
 One of the Most Powerful Wealth-Building Moves a Woman Can Make: A Midcareer Pivot
One of the Most Powerful Wealth-Building Moves a Woman Can Make: A Midcareer PivotIf it feels like you can't sustain what you're doing for the next 20 years, it's time for an honest look at what's draining you and what energizes you.
-
 I'm a Wealth Adviser Obsessed With Mahjong: Here Are 8 Ways It Can Teach Us How to Manage Our Money
I'm a Wealth Adviser Obsessed With Mahjong: Here Are 8 Ways It Can Teach Us How to Manage Our MoneyThis increasingly popular Chinese game can teach us not only how to help manage our money but also how important it is to connect with other people.
-
 Looking for a Financial Book That Won't Put Your Young Adult to Sleep? This One Makes 'Cents'
Looking for a Financial Book That Won't Put Your Young Adult to Sleep? This One Makes 'Cents'"Wealth Your Way" by Cosmo DeStefano offers a highly accessible guide for young adults and their parents on building wealth through simple, consistent habits.
-
 Global Uncertainty Has Investors Running Scared: This Is How Advisers Can Reassure Them
Global Uncertainty Has Investors Running Scared: This Is How Advisers Can Reassure ThemHow can advisers reassure clients nervous about their plans in an increasingly complex and rapidly changing world? This conversational framework provides the key.
-
 I'm a Real Estate Investing Pro: This Is How to Use 1031 Exchanges to Scale Up Your Real Estate Empire
I'm a Real Estate Investing Pro: This Is How to Use 1031 Exchanges to Scale Up Your Real Estate EmpireSmall rental properties can be excellent investments, but you can use 1031 exchanges to transition to commercial real estate for bigger wealth-building.
-
 Should You Jump on the Roth Conversion Bandwagon? A Financial Adviser Weighs In
Should You Jump on the Roth Conversion Bandwagon? A Financial Adviser Weighs InRoth conversions are all the rage, but what works well for one household can cause financial strain for another. This is what you should consider before moving ahead.