A Renewed Global Focus On Helping the Hungry
Rebounding global ag commodity prices add a sense of urgency to fighting hunger.

Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Today
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more delivered daily. Smart money moves start here.

Sent five days a week
Kiplinger A Step Ahead
Get practical help to make better financial decisions in your everyday life, from spending to savings on top deals.

Delivered daily
Kiplinger Closing Bell
Get today's biggest financial and investing headlines delivered to your inbox every day the U.S. stock market is open.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Adviser Intel
Financial pros across the country share best practices and fresh tactics to preserve and grow your wealth.

Delivered weekly
Kiplinger Tax Tips
Trim your federal and state tax bills with practical tax-planning and tax-cutting strategies.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Retirement Tips
Your twice-a-week guide to planning and enjoying a financially secure and richly rewarding retirement

Sent bimonthly.
Kiplinger Adviser Angle
Insights for advisers, wealth managers and other financial professionals.

Sent twice a week
Kiplinger Investing Weekly
Your twice-a-week roundup of promising stocks, funds, companies and industries you should consider, ones you should avoid, and why.

Sent weekly for six weeks
Kiplinger Invest for Retirement
Your step-by-step six-part series on how to invest for retirement, from devising a successful strategy to exactly which investments to choose.
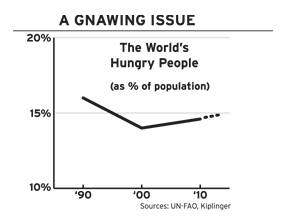
With world hunger a growing problem, the United States and other wealthy nations are stepping up to the plate with more emergency food aid as well as promises to share technology and know-how so poor countries can do more to help their farmers grow more food.
They’ve pledged to provide $22 billion by 2012, including $3.5 billion from the U.S. for food exports plus initiatives to bolster farming in poor nations. The needs are great. The number of underfed and starving people in Africa, Asia and elsewhere will stay above a billion in 2010, a level reached for the first time this year.
But the goal of rich nations to halve world hunger by 2015 is a pipe dream. Developed nations have plenty of problems at home that require attention, preventing them from doing even more to help hungry people around the world.
From just $107.88 $24.99 for Kiplinger Personal Finance
Become a smarter, better informed investor. Subscribe from just $107.88 $24.99, plus get up to 4 Special Issues

Sign up for Kiplinger’s Free Newsletters
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and more - straight to your e-mail.
Profit and prosper with the best of expert advice - straight to your e-mail.
Private interests are pitching in, too. Bayer CropScience, for example, is teaming up with Asia’s largest agricultural research institute, based in the Philippines, to form a database of more than 2,000 rice strains to speed the arrival of new varieties and fight bacterial blight. Agricultural giant Monsanto is donating its biotech savvy plus its white corn seed to help a partnership in eastern Africa develop drought tolerant varieties. And the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation has pledged $1.4 billion, with $120 million awarded in grants so far, to invest in better seeds, training, market access and policies that support small farmers. Bill Gates, the foundation’s cochair, says that “helping the poorest small-holder farmers grow more crops and get them to market is the world's single most powerful lever for reducing hunger and poverty.” The foundation’s initial grants are being targeted to produce higher yielding varieties of sorghum and millet as well as to new varieties of sweet potatoes that resist pests and have a higher vitamin content.
Rebounding global ag commodity prices will make it even harder for poor nations to feed hungry people. The index kept by the United Nations’ Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) is at its highest level since September 2008. For dairy items, it’s up 80%. Even the recent recession hasn’t had much impact on prices in poor nations, according to a second FAO index that tracks the prices of 864 basic foods in 68 developing nations. In that food market measure, prices remain about 25% higher than two years ago in two-thirds of the countries included in the index.
Note that the FAO is also actively involved in helping developing nations overcome hunger. A joint effort by the FAO and Germany, for example, has built 45,000 small silos in 16 countries for local storage of basic foods, avoiding spillage, insects and waste.
Long term, ramped-up efforts will do more than just address hunger. They’ll help developing nations to expand their wealth, which in turn will allow them to expand trade with the U.S. and other developed nations.
Profit and prosper with the best of Kiplinger's advice on investing, taxes, retirement, personal finance and much more. Delivered daily. Enter your email in the box and click Sign Me Up.

-
 Nasdaq Leads a Rocky Risk-On Rally: Stock Market Today
Nasdaq Leads a Rocky Risk-On Rally: Stock Market TodayAnother worrying bout of late-session weakness couldn't take down the main equity indexes on Wednesday.
-
 Quiz: Do You Know How to Avoid the "Medigap Trap?"
Quiz: Do You Know How to Avoid the "Medigap Trap?"Quiz Test your basic knowledge of the "Medigap Trap" in our quick quiz.
-
 5 Top Tax-Efficient Mutual Funds for Smarter Investing
5 Top Tax-Efficient Mutual Funds for Smarter InvestingMutual funds are many things, but "tax-friendly" usually isn't one of them. These are the exceptions.
-
 AI Sparks Existential Crisis for Software Stocks
AI Sparks Existential Crisis for Software StocksThe Kiplinger Letter Fears that SaaS subscription software could be rendered obsolete by artificial intelligence make investors jittery.
-
 A Scary Emerging AI Threat
A Scary Emerging AI ThreatThe Kiplinger Letter An emerging public health issue caused by artificial intelligence poses a new national security threat. Expect AI-induced psychosis to gain far more attention.
-
 An Inflection Point for the Entertainment Industry
An Inflection Point for the Entertainment IndustryThe Kiplinger Letter The entertainment industry is shifting as movie and TV companies face fierce competition, fight for attention and cope with artificial intelligence.
-
 Humanoid Robots Are About to be Put to the Test
Humanoid Robots Are About to be Put to the TestThe Kiplinger Letter Robot makers are in a full-on sprint to take over factories, warehouses and homes, but lofty visions of rapid adoption are outpacing the technology’s reality.
-
 Trump Reshapes Foreign Policy
Trump Reshapes Foreign PolicyThe Kiplinger Letter The President starts the new year by putting allies and adversaries on notice.
-
 Congress Set for Busy Winter
Congress Set for Busy WinterThe Kiplinger Letter The Letter editors review the bills Congress will decide on this year. The government funding bill is paramount, but other issues vie for lawmakers’ attention.
-
 The Kiplinger Letter's 10 Forecasts for 2026
The Kiplinger Letter's 10 Forecasts for 2026The Kiplinger Letter Here are some of the biggest events and trends in economics, politics and tech that will shape the new year.
-
 Disney’s Risky Acceptance of AI Videos
Disney’s Risky Acceptance of AI VideosThe Kiplinger Letter Disney will let fans run wild with AI-generated videos of its top characters. The move highlights the uneasy partnership between AI companies and Hollywood.